慢性肾病:美国在研的130项基金项目,关注这些热点(2024)
2024-11-05 Hanson临床科研 Hanson临床科研 发表于上海
我们仅对美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)资助的在研慢性肾病相关项目进行梳理,希望给同仁们的选题思路提供一点启发。
慢性肾病(Chronic Kidney Disease,简称CKD),是一种逐渐丧失肾脏功能的疾病。随着疾病的进展,肾脏逐渐无法清除血液中的废物和多余水分,无法维持体内环境的稳定,最终可能发展到肾衰竭,需要透析或肾脏移植。
尽管近年来在慢性肾病的诊断和治疗方面取得了显著进展,但仍存在一些重要而未解决的临床问题:
-
早期诊断:许多患者在早期阶段没有明显症状,常常在病情发展到较严重阶段才被发现。需要更有效的筛查和监测方法来早期诊断和干预。
-
治疗选择:尽管有透析和肾脏移植等治疗方法,但这些治疗并不能逆转肾脏损伤,而且透析患者的生活质量受到严重影响,肾脏移植的供体也十分有限。
-
并发症管理:慢性肾病患者常常伴有高血压、糖尿病等其他疾病,需要综合治疗和管理,并发症的控制是提高患者预后的关键。
-
肾脏保护:目前缺乏有效的药物可以停止或逆转肾功能衰退的进程。研发新的药物和治疗策略,以保护肾脏功能,延缓疾病进程是研究的热点。
慢性肾病的治疗和管理需要长期的医疗跟踪和生活方式的调整,以减缓疾病进程和提高患者生活质量。未来的研究需要聚焦于开发新的治疗方法,以及改善早期诊断和监测技术。
我们仅对美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)资助的在研慢性肾病相关项目进行梳理,希望给同仁们的选题思路提供一点启发。
2024年,以“Chronic Kidney Disease”为检索词、在题目中进行检索,美国NIH针对慢性肾病的在研有130项。
一,谁获得了这些研究?
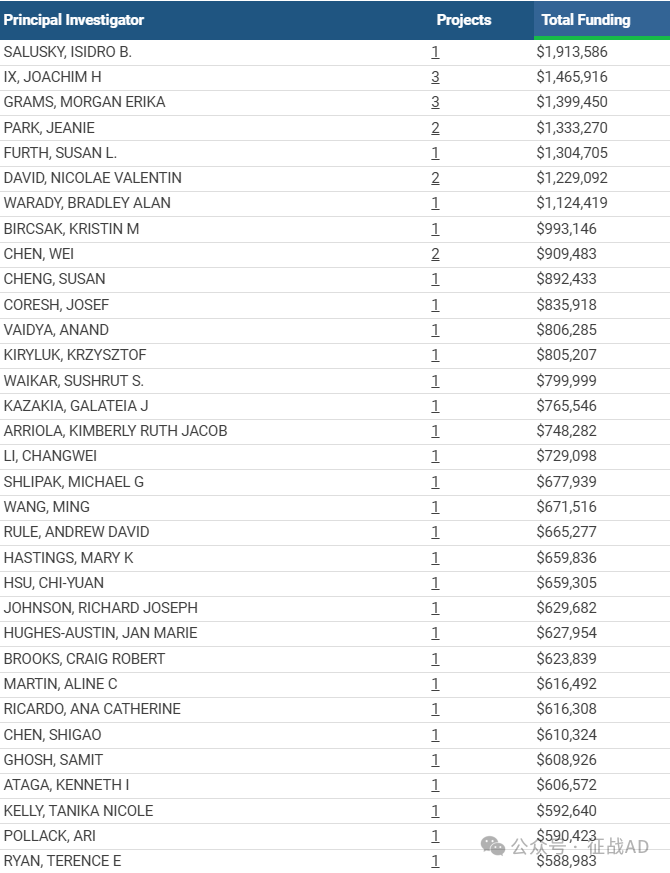
1,在研慢性肾病基金最多的PI
-
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA LOS ANGELES 的 SALUSKY, ISIDRO B.
-
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA LOS ANGELES 的 IX, JOACHIM H
-
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA LOS ANGELES 的 GRAMS, MORGAN ERIKA
-
EMORY UNIVERSITY 的 PARK, JEANIE
-
CHILDREN'S HOSP OF PHILADELPHIA 的 FURTH, SUSAN L.
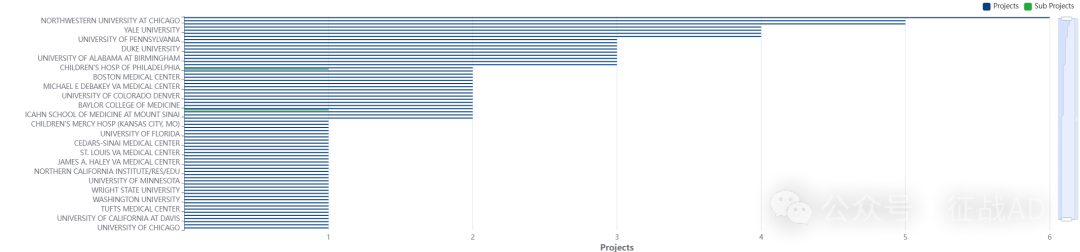
2,慢性肾病基金最多的研究机构
-
纽约大学医学院
-
加州大学洛杉矶分校
-
芝加哥西北大学
-
埃默里大学
-
罗切斯特梅奥诊所等
二,慢性肾病研究热点是什么?
慢性肾病研究领域总览(根据关键词)
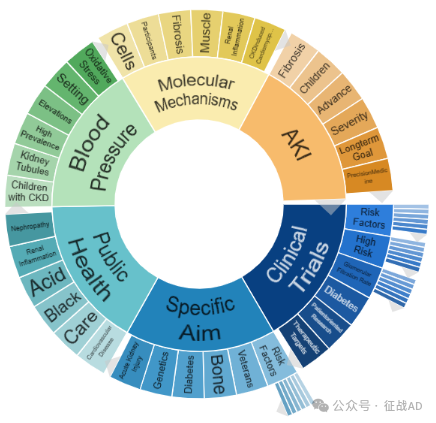
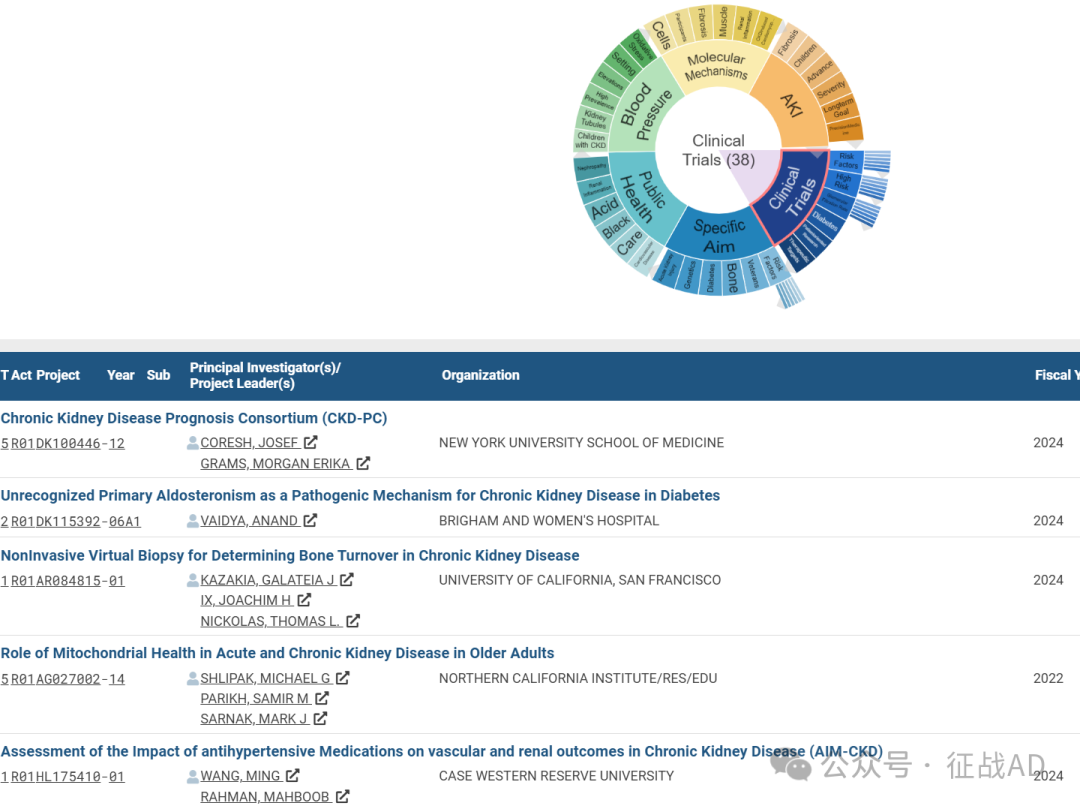
A,关于临床研究(Clinical Trials)的研究项目最多
有 38 项在研基金涉及到了临床研究,关注最多的方面包括风险因素(Risk Factors)、高风险(High Risk)、肾小球滤过率(Glomerular Filtration Rate)、糖尿病(Diabetes)、以患者为导向的研究(Patientoriented Research)、治疗靶点(Therapeutic Targets)等方面研究。
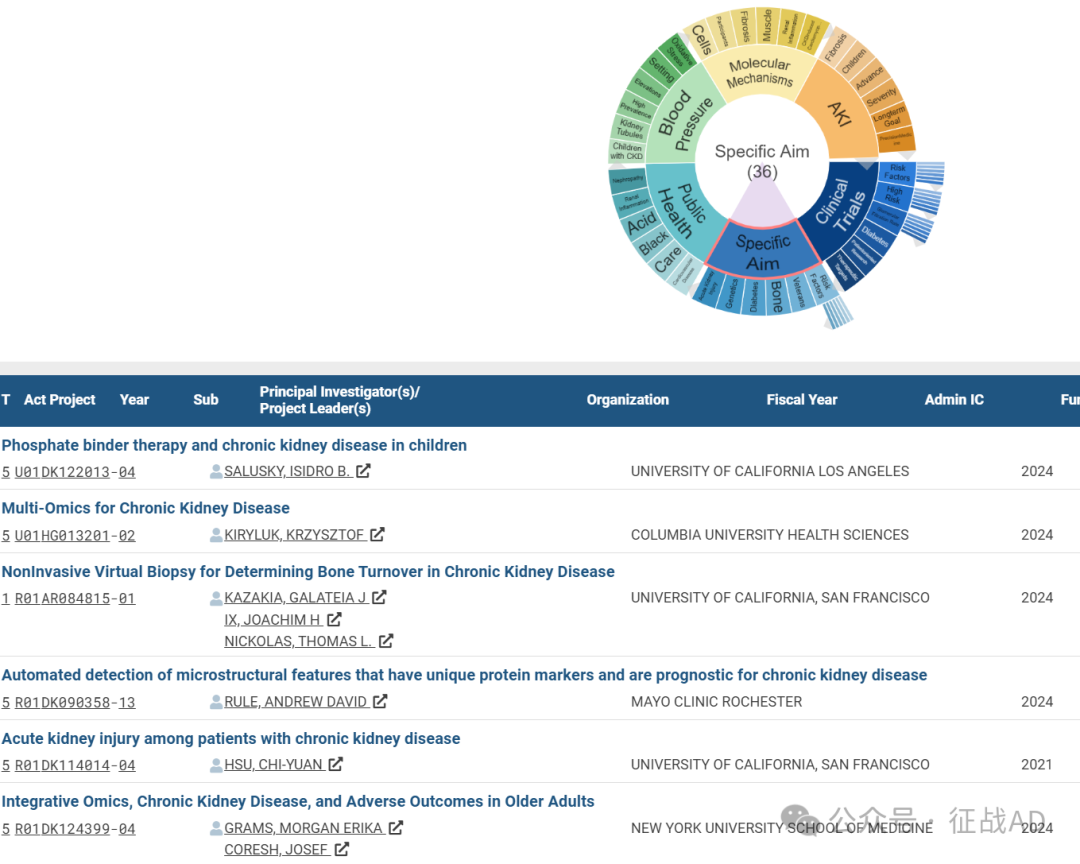
B,具体目标(Specific Aim)的研究
有 36 项研究涉及到具体目标,研究领域主要涉及风险因素(Risk Factors)、(Veterans)、骨骼(Bone)、糖尿病(Diabetes)、遗传学(Genetics)、急性肾损伤(Acute Kidney Injury)等方面研究。
C,公共卫生(Public Health)
有 20 项研究涉及到公共卫生,涉及的关键词包括心血管疾病(Cardiovascular Disease)、护理、酸(Acid)、肾炎(Renal Inflammation)、肾病(Nephropathy)等。
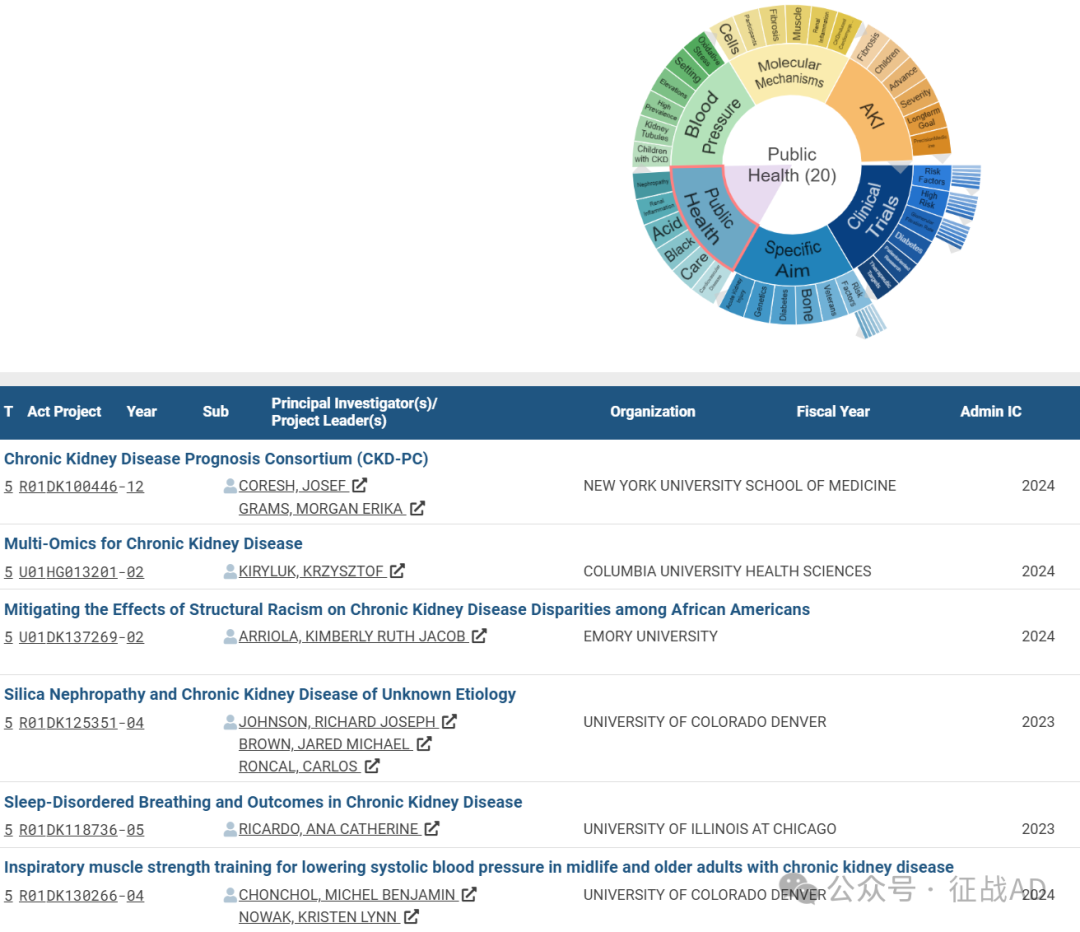
其他慢性肾病研究大的方向也包括血压(Blood Pressure)、AKI、分子机制(Molecular Mechanisms)等。
三,借鉴与突破
我们也分享在慢性肾病领域的几项课题摘要,希望对同仁们有所启发。
A,Phosphate binder therapy and chronic kidney disease in children
Therefore, we hypothesize that treatment with FC will lower intact FGF23 levels during a 12-month period in a randomized, double-blinded, two -arms parallel study in 160 pediatric patients with CKD stages 3-4 and normal serum phosphate levels.
The multi-site trial will pursue the following specific aims:
Specific Aim 1: To determine the efficacy of FC to lower serum intact FGF23 levels (primary endpoint) in pediatric patients with CKD 3–4 over 12 months.
Specific Aim 2: To determine the effects of the interventions on anemia, kidney function, and indices of bone and mineral metabolism (secondary end-points). Additionally, we will perform pre- and post-treatment bone biopsies to assess bone histomorphometry and FGF23 expression in a sub-cohort of 24 UCLA patients.
Specific Aim 3: To determine the safety and tolerability of FC in pediatric CKD 3-4 patients. If our hypothesis is confirmed, then a new treatment paradigm would emerge in which therapy with FC will be initiated early in CKD, when patients are normophosphatemic, slowing progressive increases in FGF23 and blunting FGF23-associated adverse renal and CVD.
B, Development of the NephroPlate: A high-throughput kidney-on-a-chip platform for identifying chronic kidney disease therapies
Together we will focus on addressing the market need for a 3D kidney-on-a-chip platform, called the NephroPlate for use in drug discovery. The NephroPlate will enable the evaluation of kidney function in response to circulating and genetic factors of CKD-causing disorders.
For this Phase II project, we will focus on glomerulopathies where we have previous experience, Alport syndrome and membranous nephropathy, and where there is a high demand from NephroPlate customers, diabetic nephropathy and APOL1 nephropathy. For each CKD, we will characterize phenotype (immunostaining, western blot, RNAseq) and glomerular filtration function by measuring the passage of fluorescent albumin and the trans-epithelial electrical resistance (TEER) within the microfluidic system. All systems will be validated to high-throughput drug screening standards. Filtrate from the glomerulus-on-a-chip cultures will be transferred to the proximal tubule-on-a-chip cultures to evaluate the impact of glomerular disease on proximal tubules. Finally, proteomics will be performed on the glomerular and proximal tubule filtrate to identify potential biomarkers specific to each CKD.
Once executed these studies will establish the NephroPlate as a high-throughput drug screening platform for use by pharmaceutical companies and academic laboratories to investigate mechanisms of CKD diseases and ultimately identify disease-specific therapeutics.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言














#慢性肾病# #美国国立卫生研究院#
20