【论著】| Circ-0007766作为miR-1972海绵调控HER2表达促进乳腺癌细胞迁移和侵袭
2024-11-21 中国癌症杂志 中国癌症杂志 发表于陕西省
本研究旨在探讨Circ-0007766作为miR-1972海绵调控HER2表达对乳腺癌细胞迁移和侵袭的影响。
[摘要]背景与目的:人表皮生长因子受体2(human epidermal growth factor receptor 2,HER2)是乳腺癌最重要的转移驱动因子之一,20%~30%的乳腺癌患者为HER2高表达型。HER2的表达水平可以在多个分子层面受到调控并且决定了乳腺癌细胞的转移潜能,但HER2的表达如何在mRNA水平受到调控仍不清楚。Circ-0007766是源自HER2的编码基因酪氨酸激酶受体2(tyrosine kinase receptor 2,ERBB2)形成的circRNA,circ-0007766能否通过内源竞争RNA(competing endogenous RNAs,ceRNA)机制调控HER2表达仍鲜见报道。本研究旨在探讨Circ-0007766作为miR-1972海绵调控HER2表达对乳腺癌细胞迁移和侵袭的影响。方法:本研究使用高通量circRNA芯片筛选出在HER2阳性乳腺癌细胞中表达特异性高表达的circRNA;采用荧光原位杂交实验(fluorescence in situ hybridization,FISH)检测circ-0007766的亚细胞定位;采用microRNA检测原位杂交(BaseScope)实验分析circ-0007766在乳腺癌组织中的表达水平及其临床诊断意义;通过体外转染克隆质粒和siRNA构建过表达和敲低circ-0007766的乳腺癌细胞模型;采用transwell实验评估circ-0007766对乳腺癌细胞迁移和侵袭能力的影响,测定MDA-MB-231与SK-BR-3细胞的迁移和侵袭能力,并用transwell实验评估circ-0007766能否通过 miR-1972促进乳腺癌细胞的迁移和侵袭能力。利用双荧光素酶报告基因检测验证circ-0007766能否通过结合miR-1972调控HER2的表达。通过RNA反义纯化(RNA antisense purification,RAP)实验进一步验证circ-0007766和miR-1972是否具有直接相互作用;在 MDA-MB-231细胞中进行RNA免疫沉淀(RNA immunoprecipitation,RIP)检测,并通过实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction,RTFQ-PCR)测定 HER2 mRNA的相对3'UTR。采用蛋白质印迹法(Western blot)检测蛋白表达情况。结果:circ-0007766在HER2阳性乳腺癌细胞中高表达,circ-0007766分布于细胞质和细胞核,并且主要分布于细胞质。Circ-0007766在乳腺癌组织中的表达水平显著高于癌旁组织,在HER2阳性乳腺癌中表达显著升高,且在HER2阳性乳腺癌样本中的表达水平显著高于HER2阴性样本。在HER2阴性乳腺癌细胞中过表达(在HER2阳性乳腺癌细胞中敲低)circ-0007766能够促进(抑制)乳腺癌细胞的迁移和侵袭能力。Circ-0007766与抑制乳腺癌细胞迁移和侵袭的miR-1972直接结合,形成ceRNA调控网络,抑制由miR-1972介导的HER2 mRNA和蛋白表达水平下调。Circ-0007766能够上调由miR-1972负调控HER2介导的乳腺癌细胞迁移和侵袭的抑制作用。CircRNA通过封存miRNA发挥ceRNA的功能,从而在转录和翻译水平上调控基因表达。最后,我们发现circ-0007766和HER2在乳腺癌细胞和组织样本中的表达呈正相关,而miR-1972和HER2的表达水平呈负相关。Circ-0007766 能特异性靶向miR-1972,从而阻碍miR-1972对HER2表达的调控作用。结论:本研究发现circ-0007766通过miR-1972/HER2信号轴促进乳腺癌细胞的迁移和侵袭,为转移性HER2阳性乳腺癌患者提供了一个新的生物标志物和潜在治疗靶点。
[关键词] 乳腺癌;人表皮生长因子受体2;circ-0007766;miR-1972;转移
[Abstract]Background and purpose: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) serves as one of the paramount drivers of breast cancer metastasis, with roughly 20%-30% of breast cancer patients exhibiting high expression of HER2. The expression level of HER2 is regulatable at multiple molecular levels and determines the metastatic potential of breast cancer cells; however, the manner in which HER2 expression is modulated at the mRNA level remains ambiguous. Circ-0007766 is a circRNA originated from the coding gene ERBB2 for HER2, and whether circ-0007766 can regulate HER2 expression via the ceRNA mechanism has not been reported. This study aimed to analyze whether circ-0007766 acts as a miR-1972 sponge to promote breast cancer cell migration and invasion via upregulation of HER2 expression. Methods: In this study, a high-throughput circRNA chip was employed to screen for circRNAs that exhibited highly specific expression in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was utilized to detect the subcellular localization of circ-0007766. The BaseScope experiment was conducted to analyze the expression level of circ-0007766 in breast cancer tissues and its clinical diagnostic significance. Breast cancer cell models with overexpression and knockdown of circ-0007766 were constructed by transfecting cloning plasmids and siRNA in vitro. The effect of circ-0007766 on the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells was assessed using transwell migration and invasion experiments, and the migration and invasion abilities of MDA-MB-231 and SK-BR-3 cells were measured. Additionally, it was evaluated whether circ-0007766 could promote the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells through miR-1972. A dual luciferase reporter gene assay was used to verify whether circ-0007766 could regulate HER2 expression by binding to miR-1972. The direct interaction between circ-0007766 and miR-1972 was further verified through the RAP experiment. RIP detection was performed in MDA-MB-231 cells, and the relative 3'UTR of HER2 mRNA was measured by real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RTFQ-PCR). Western blot was used to detect the protein expressions. Results: Circ-0007766 was conspicuously highly expressed in HER2-positive breast cancer cells and distributed in both the cytoplasm and nucleus of cells, with the preponderance being in the cytoplasm. The expression level of circ-0007766 was strikingly higher in breast cancer tissues than in para-cancerous tissues. The expression of circ-0007766 was significantly elevated in HER2-positive breast cancer samples compared with HER2-negative samples. The overexpression (knockdown) of circ-0007766 in HER2-negative breast cancer cells (in HER2-positive breast cancer cells) was capable of promoting (inhibiting) the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. Circ-0007766 directly bound to miR-1972, which inhibited breast cancer cell migration and invasion, thereby forming an endogenous competitive RNA (ceRNA) regulatory network and impeding the downregulation of HER2 mRNA and protein expression mediated by miR-1972. Circ-0007766 could potentiate the inhibitory effect of miR-1972 on HER2-mediated breast cancer cell migration and invasion that was negatively regulated by miR-1972. CircRNAs sequestered miRNAs to function as ceRNAs, thereby regulating gene expression at both the transcriptional and translational levels. Finally, we discovered that the expressions of circ-0007766 and HER2 were positively correlated in breast cancer cell and tissue samples, while the expression levels of miR-1972 and HER2 were negatively correlated. Circ-0007766 could specifically target miR-1972 to hinder its regulatory effect on HER2 expression. Conclusion: This study discovers that circ-0007766 facilitates the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells via the miR-1972/HER2 signal axis, offering a novel biomarker and potential therapeutic target for patients with metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer.
[Keywords] Breast cancer; Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; circ-0007766; miR-1972; Metastasis
乳腺癌是一种高度异质性的恶性肿瘤,根据雌激素受体(estrogen receptor,ER)、孕激素受体(progesterone receptor,PR)、人表皮生长因子受体2(human epidermal growth factor receptor 2,HER2)的表达情况和Ki-67增殖指数进行分子分型[1-3]。20%~30%的乳腺癌患者为HER2高表达型,易发生淋巴结转移或脑转移,并且复发转移率高、患者预后较差。尽管目前多种抗HER2的靶向治疗药物已在临床上广泛使用,使得HER2阳性乳腺癌的治疗策略得到不断优化,但是单药靶向治疗时仍有50%的患者发生耐药[4-6]。为了改善HER2阳性乳腺癌的治疗现状,有必要阐明HER2阳性型乳腺癌发生、发展的分子机制。
HER2是HER/ERBB家族成员之一,能与激活的任一HER家族成员形成异二聚体[7],促进细胞内酪氨酸激酶结构域激活,级联激活磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(phosphoinositide3-kinase,PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(protein kinase,AKT)和Ras/Raf/MEK/MAPK等信号转导通路[8],导致细胞增殖、迁移、浸润,并促进血管生成,在HER家族信号转导通路中处于核心地位。HER2阳性乳腺癌的早期播散癌细胞前体可通过激活Wnt信号转导通路,在不完全丧失上皮表型的情况下局部侵袭组织、侵入血管并潜伏在靶器官中,然而,这一过程可以通过抑制Wnt或HER2而逆转[9]。在乳腺上皮祖细胞中,表皮生长因子受体通过促进上皮-间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transformation,EMT)来抑制HER2介导的癌变,从而起到抑制肿瘤的作用[10]。相反,EMT过程中金属蛋白酶的表达和激活增加会导致HER2受体蛋白水解和脱落,从而下调HER2细胞外结构域,最终增加曲妥珠单抗的耐药性[11]。
HER2(ERBB2)的表达水平可在基因突变、基因转录、mRNA翻译和蛋白质修饰等多个环节受到调控。CircRNA作为miRNA分子海绵在靶基因mRNA表达调控及肿瘤增殖、转移、血管生成、免疫等方面发挥重要作用。Circ-CCDC9通过miR-6792-3p/CAV1轴抑制胃癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭,从而抑制胃癌的进展,成为胃癌的一个可开发的生物标志物和治疗靶点[12]。CircTADA2A-E6作为miR-203a-3p海绵,能够挽救靶基因SOCS3的表达,从而削弱乳腺癌的侵袭性[13]。然而,在乳腺癌细胞中HER2作为靶基因如何受到circRNA/miRNA形成的内源竞争RNA(competing endogenous RNA,ceRNA)调控的机制仍不清楚。
Circ-0007766是源自HER2的编码基因ERBB2形成的circRNA。Circ-0007766能够编码一段短肽(HER2-103)。HER2-103诱导EGFR同源二聚体或EGFR/HER3异源二聚体的形成,激活PI3K-AKT下游信号转导通路,促进乳腺癌增殖和发展。并且帕妥珠单抗可结合HER2-103的CRI结构域而增强三阴性乳腺癌(triple-negative breast cancer,TNBC)对帕妥珠单抗的敏感性[14]。此外,circ-0007766通过miR-1233-3p/GDF15轴可抑制胃癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭[15]。Circ-0007766还能够通过上调细胞周期相关蛋白cyclin D1/cyclin E1/CDK4的表达促进肺腺癌细胞增殖[16]。然而,circ-0007766能否通过ceRNA机制调控HER2表达仍鲜见报道。
MiR-1972广泛参与肿瘤的生长和转移,发挥抑癌基因作用。MiR-1972在卵巢癌组织中高表达,LINC01125通过直接结合miR-1972,调节细胞凋亡途径,进而增强卵巢癌细胞对顺铂的敏感性[17]。LINC01207通过与miR-1972结合,上调LASP1的表达,能够促进前列腺癌细胞的生长和转移[18]。而在骨肉瘤细胞中,miR-1972与lncRNA DANCR形成ceRNA调控网络,lncRNA DANCR能够恢复由miR-1972介导的ROCK1表达下调,从而促进肿瘤细胞增殖和转移[19]。
本研究旨在探讨Circ-0007766作为miR-1972海绵调控HER2表达对乳腺癌细胞迁移和侵袭的影响。
1 材料和方法
1.1 细胞和试剂
人正常乳腺上皮细胞(MCF-10A)和人乳腺癌细胞(MDA-MB-231、MCF-7、BT-474、SK-BR-3、UACC-812)购自中国科学院典型培养物保藏委员会细胞库。DMEM、RPMI-1640、Opti-MEM及胎牛血清培养基购自美国Gibco公司。LipofectamineTM 3000 Transfection Reagent购自美国ThermoFisher公司。SYBR Green购自日本TaKaRa公司。稳定过表达circ-0007766细胞及其对照细胞、circ-0007766 non-ATG质粒由南昌聚焦生物科技有限公司构建。RNA荧光原位杂交实验(fluorescence in situ hybridization experiment,FISH)试剂盒购自广州锐博生物科技有限公司。BaseScope二代红色试剂盒(伦理审批编号:323900)购自美国ACD公司。乳腺癌组织芯片(伦理审批编号:HBreD139Su01)及乳腺癌旁组织芯片(HBre-Duc090Sur-01)购自上海芯超生物科技有限公司。
1.2 细胞培养
MDA-MB-231、MCF-7、SK-BR-3、UACC-812用DMEM(美国Gibco公司)培养,BT-474用RPMI-1640(美国Gibco公司)培养,MCF-10A用MCF-10A专用培养基(武汉普赛诺生命科技有限公司)培养。所有细胞培养基均加入10%的胎牛血清和1%的青链霉素混合液。细胞在37 ℃、 CO2体积分数为5%的培养箱中进行培养,隔天换液,细胞汇合度达到80%~90%时传代。
1.3 CircRNA芯片
用NanoDrop ND-1000微量分光光度计分析MCF-10A、MDA-MB-231、MCF-7和SK-BR-3细胞系的总RNA。按照Arraystar的标准协议,我们制备了样本并进行了微阵列杂交。在消化总RNA 时加入RNase R(Epicenter, Inc.)后,用随机引物法(Arraystar Super RNA Labeling Kit)将富集的环状RNA扩增和转录为荧光cRNA。标记后,cRNA在Arraystar Human circRNA Array V2(8×15K,Arraystar)上进行杂交处理。清洗玻片后,使用安捷伦扫描仪G2505C进行阵列扫描。使用安捷伦特征提取软件(11.0.1.1版)分析获得的阵列图像。两组间表达差异显著的circRNA通过火山图确定,而两份样本间表达差异显著的circRNA则根据折叠变化确定。样本间circRNA差异表达模式通过分层聚类显示出来。
1.4 FISH检测
使用4%的多聚甲醛固定SK-BR-3细胞20 min,然后在预冷的0.5% Triton X-100中进行细胞通透处理,在37 ℃下进行探针预杂交和探针杂交。利用DAPI对细胞核染色20 min。玻片用适量抗荧光淬灭剂封片,避光,置于荧光显微镜下观察和拍照。
1.5 基准范围
在研究伦理委员会的指导下,共有133份乳腺癌组织芯片(包括32份TNBC、26份HER2、47份管腔A、28份管腔B)和89份癌旁组织的组织芯片接受了该检测方法的评估。将乳腺癌组织芯片烘烤60 min,然后用二甲苯和无水乙醇脱蜡20 min,再用过氧化氢处理10 min,然后在98~102 ℃下进行抗原回收。蛋白酶处理15~30 min后,用APM1-8试剂温育切片以放大信号。用蒸馏水冲洗后,用0.02%的氨水重新染色,再用蒸馏水清洗。然后将切片干燥,并根据组织芯片的大小用适当的VectaMount密封液密封。最后,扫描整个芯片,并使用QuPath软件分析信号强度。信号点大于2为circ-0007766高表达。
1.6 Transwell实验
在transwell下室加入500 μL完全培养基,用无血清培养基重悬的20万细胞并加入transwell上室,置于37 ℃,CO2体积分数为5%的温箱中温育24 h。弃掉小室内培养基后利用多聚甲醛固定细胞,结晶紫染色,使用中性树胶对样本进行封片。通过显微镜观察和拍摄结果,并利用Image J软件分析迁移细胞的数量。
1.7 实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(RTFQ-PCR)
用TRIzol法提取细胞总RNA,利用分光分度计检测总RNA浓度。用PrimeScript RT试剂盒反转录合成cDNA。以GAPDH作为内参,BIO-RAD荧光定量PCR仪上SYBR Green染料试剂盒检测待测基因的表达水平。
1.8 蛋白质印迹法(Western blot)检测
收集转染48 h后的MDA-MB-231细胞,每组加入200 μL 放射免疫沉淀法(radio immunoprecipitation assay,RIPA)裂解液(PMSF∶RIPA=1∶100)后提取各组细胞总蛋白,每孔按20 μg蛋白进行上样,进行十二烷基硫酸钠聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(sodium dodecylsulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, SDS-PAGE)后将蛋白转移到聚偏二氟乙烯(polyvinylidene fluoride,PVDF)膜上,5%脱脂奶粉封闭3 h,然后依次温育一抗和二抗。经电化学发光(electrochemical luminescence,ECL)显色,在OI 900全自动化学发光成像仪内拍照,并用Image J对图像进行分析。
1.9 RAP实验
收集4×107个SK-BR-3和MDA-MB-231细胞,PBS洗涤后用1%的甲醛交联细胞,加入细胞裂解液冰上裂解10 min。加入DNase 37 ℃温育10 min后转冰浴,65 ℃变性。取探针总量为n×40 pmol(n为探针条数),85 ℃变性3 min后,快速转移至冰浴,转移至细胞裂解液中37 ℃杂交3 h。按n×10 μL取探针用杂交缓冲液颠倒洗涤,加入样本中室温结合30 min,冲洗缓冲液洗涤,RNA洗脱缓冲液洗脱收集RNA后进行RTFQ-PCR分析。
1.10 双荧光素酶报告基因实验
在HEK-293T细胞中分别转染miRNA mimics、NC mimics、circ-0007766的3'UTR双报告基因载体及突变载体。转染48 h后吸出培养基,以加入萤光素酶试剂35 μL/孔,振荡10 min,转移至96孔板中,以分光光度计测定荧光值。每孔加入30 μL终止试剂,振荡10 min,再次检测荧光值。
1.11 抗Ago2 RNA免疫沉淀(RNA immuno-precipitation,RIP)实验
将miR-NC或miR-1972转染至MDA-MB-231细胞。转染36 h后,采用Magna RIPTM RNA结合蛋白免疫沉淀试剂盒对转染细胞进行RIP检测。6组细胞分别与阴性对照IgG或抗iago2抗体温育。RTFQ-PCR检测ERBB2的相对表达量。
1.12 统计学处理
实验数据表示为至少3个生物学重复的样本均数。定性变量用χ2检验,对于两组定量资料分析比较,若满足正态分布,且满足方差齐性,采用独立样本t检验,以均x±s表示;只满足正态分布,不满足方差齐性,采用Welch’s校正非配对t检验,以x±s表示;不满足正态分布,则采用Mann-Whitney U检验,用中位数和四分位数间距表示。分析数据每个组之间的特有和共有的部分,并且用ggplot2包和VennDiagram包对结果进行可视化制作韦恩图。生存曲线采用Kaplan-Meier法,组间比较采用log-rank检验。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。采用SPSS 22.0软件对数据进行统计分析。
2 结 果
2.1 Circ-0007766在HER2阳性乳腺癌细胞中表达上调
为了筛选在HER2阳性乳腺癌细胞中表达水平较高的circRNA,我们利用乳腺癌细胞SK-BR-3(HER2+)、MCF-7(Luminal型)、MDA-MB-231(TNBC)和正常乳腺细胞MCF-10A开展高通量circRNA芯片实验(图1A)。获得标准化的circRNA表达数据。以log2丨FC丨≥2且P<0.05为筛选标准,我们获得了SK-BR-3 vs MCF-10A,MCF-7 vs MCF-10A和MDA-MB-231 vs MCF-10A的差异表达circRNA。与MCF-10A相比,circRNA在SK-BR-3中上调845个,下调997个;在MCF-7中上调973个,下调793个;在MDA-MB-231中上调938个,下调1 054个(图1B~D)。我们在SK-BR-3上调的circRNAs中去除同时在MCF-7和MDA-MB-231中上调的circRNAs,但保留了SK-BR-3 vs MCF-10A对比组中被认为是仅在HER2阳性乳腺癌细胞中表达上调的circRNA。在515个SKBR3特异性高表达circRNA中,我们进一步获得了10个差异表达倍数最大的circRNA(图1E)。其中circ-0003910在HER2阳性乳腺癌细胞中表达上调,能够促进HER2阳性乳腺癌细胞迁移和侵袭[20];此外, circ-0001598可能是治疗HER2阳性乳腺癌的靶点,circ-0001598对乳腺癌发挥促癌基因作用,circ-0001598/miR-1184/PD-L1信号失调促进了HER2阳性乳腺癌细胞的增殖和侵袭性[21]。Circ-0007766是由人类第17号染色体上的ERBB2基因的第6~10号外显子环化而成的,长度为676 nt(图1F)。鉴于circ-0007766的形成来源于HER2的亲本编码基因ERBB2,我们认为circ-0007766具有潜在研究价值。我们通过RTFQ-PCR测定,circ-0007766在6种乳腺癌细胞系和MCF-10A细胞中的表达水平,检测结果表明,circ-0007766在SK-BR-3中的表达上调幅度最高(图1G)。为了研究circ-0007766的亚细胞定位,我们在SK-BR-3细胞中进行了FISH实验,结果表明,circ-0007766分布于细胞质和细胞核,但主要定位于细胞质(图1H)。
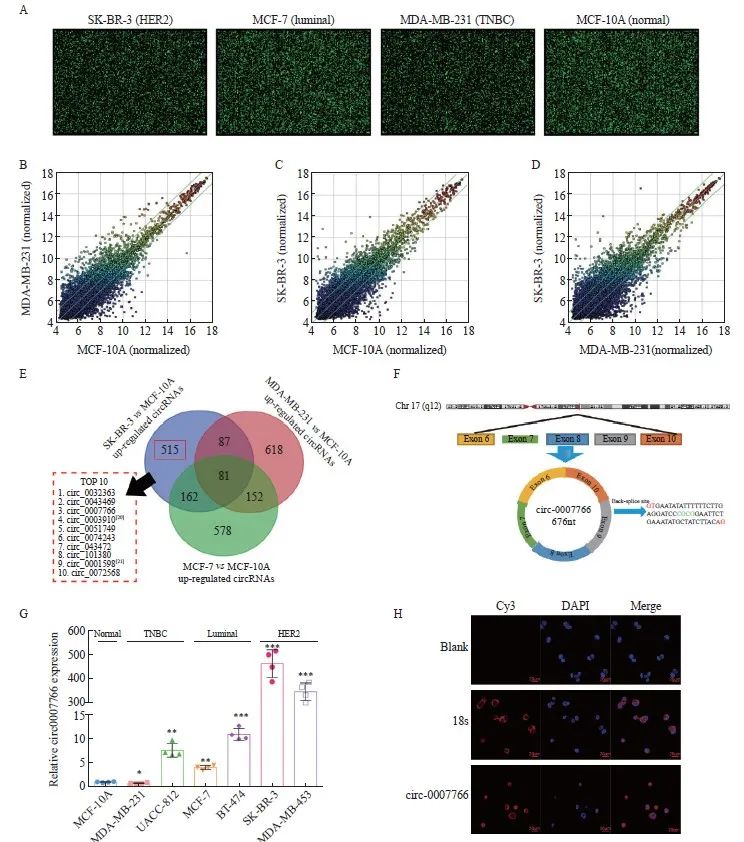
图1 Circ-0007766在HER2阳性乳腺癌细胞中的表达增加
Fig. 1 Circ-0007766 expression increased within HER2-positive breast cancer cells
A: The original images of circRNA expression in different breast cancer cells were shown by circRNA microarray. B: Scatter plots showed the differential expression of circRNA in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-10A cells. C: Scatter plots showed the differential expression of circRNA in MCF-7 and MCF-10A cells. D: Scatter plots showed the differential expression of circRNA in SK-BR-3 and MCF-10A cells. E: A Venn diagram showed the differential expression of circRNAs in different breast cancer cells and normal breast cancer cells. F: Chromosomal location and loop formation of circ-0007766. G: The expression of circ-0007766 was determined by RTFQ-PCR in 6 breast cancer cell lines and MCF-10A cells. H: Circ-0007766 was detected by FISH in the subcellular location of SK-BR-3 cells. *: P<0.05, compared with the normal breast cell MCF-10A group; **: P<0.01, compared with the normal breast cell MCF-10A group;***: P<0.001 compared with the normal breast cell MCF-10A group.
2.2 Circ-0007766在HER2阳性乳腺癌组织中高表达
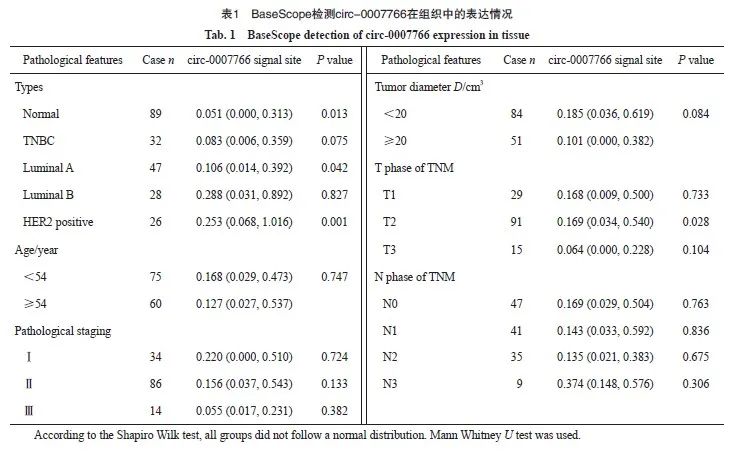
为了进一步验证circ-0007766在乳腺癌组织中的表达水平及其临床诊断价值,我们利用133例乳腺癌组织和89例癌旁组织开展BaseScope实验。结果显示,circ-0007766在乳腺癌组织中的表达水平显著高于乳腺正常组织,尤其在HER2阳性乳腺癌中表达显著升高(图2A ~C)。为了进一步探讨circ-0007766在乳腺癌中高表达的临床意义,我们分析了circ-0007766的表达水平与各项临床病理指标的相关性。结果表明,除T2期(P=0.028)外,circ-0007766与预后(P=0.484)、年龄、肿瘤大小及病理学分级(P>0.05)均无显著相关(表1)。
2.3 Circ-0007766促进乳腺癌细胞的迁移和侵袭
由于HER2阳性乳腺癌细胞表现出更强的侵袭和转移能力,我们首先评估了circ-0007766对乳腺癌细胞迁移和侵袭潜力的影响。发现circ-0007766在TNBC细胞MDA-MB-231中的表达水平最低,而在HER2阳性细胞SK-BR-3中的表达水平最高(图1F),这促使我们研究circ-0007766在MDA-MB-231中的过表达和在SK-BR-3中的敲低[22]。我们通过RTFQ-PCR分析证实了circ-0007766在MDA-MB-231细胞中的成功过表达(图3A),并且使用siRNA在SK-BR-3细胞中显著敲低circ-0007766(图3C)。与对照组相比,circ-0007766能促进MDA-MBA-231的侵袭和迁移(图3B)。此外,敲低circ-0007766能显著抑制SK-BR-3细胞的侵袭和迁移(图3C、D)。因此,我们证明了circ-0007766的过表达(敲除)能促进(抑制)乳腺癌细胞的迁移和侵袭。
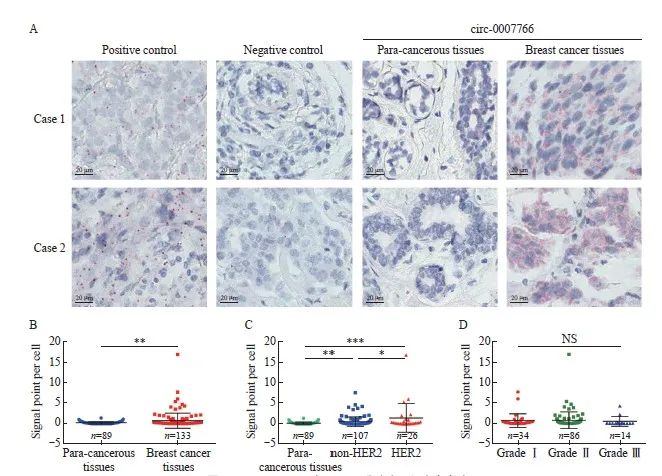
图2 Circ-0007766在HER2乳腺癌组织中高表达
Fig. 2 Circ-0007766 showed high expression within HER2 breast cancer tissues
A: BaseScope displayed representative images of the expression and localization of circ-0007766 in breast cancer and para-cancerous tissue. B: Scatter plot of circ-0007766 expression in breast cancer and para-cancerous tissues. C: Scatter plot of circ-0007766 levels in HER2-positive and HER2-negative breast cancer tissues. D: Scatter plot of circ-0007766 expression in breast cancer of different clinical grades. *: P<0.05, compared with non-HER2; **: P<0.01, compared with each other; ***: P<0.001, compared with each other; NS: Without statistically significant meaning.
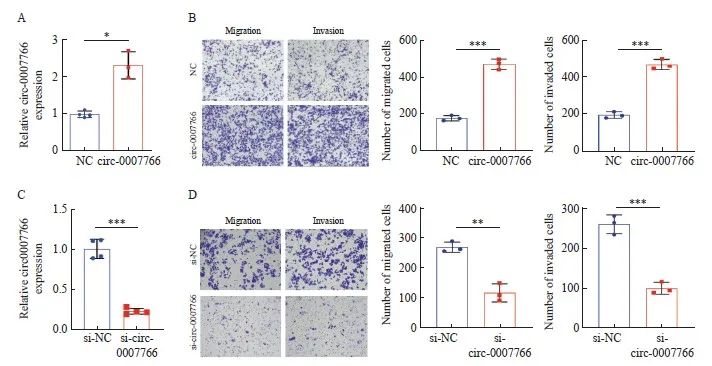
图3 Circ-0007766促进乳腺癌细胞体外侵袭和迁移
Fig. 3 Circ-0007766 promotes breast cancer cell invasion and migration in vitro
A: The level of circ-0007766 in MDA-MB-231 cells was detected by RTFQ-PCR after transfection with circ-0007766 or NC plasmid. B: The number of migrating and invasive MDA-MB-231 cells was shown by transwell assay after transfection with circ-0007766 or NC plasmid. C: The expression of circ-0007766 in SK-BR-3 cells after transfection with si-circ-0007766 or si-NC plasmid. D: The number of migrating and invasive cells in SK-BR-3 cells after transfection with si-NC and si-circ-0007766 plasmid was shown by transwell assay. *: P<0.05, compared with NC; **: P<0.01, compared with si-NC; ***: P<0.001, compared with NC or si-NC.
2.4 Circ-0007766与miR-1972相互作用,抑制乳腺癌细胞的迁移和侵袭。
为了验证circ-0007766能否通过ceRNA机制调控HER2的表达,我们运用miRWalk2.0预测靶向HER2的miRNA,共发现18个miRNA-HER2关系对在miRWalk(http://mirwalk.umm.ni-heidelberg.de/)、miRand(http://www. microrna.org/microrna/home.do)、RNA22(https://cm.jefferson.edu/rna22-full-sets-of-predictions/)和Targetscan(https://www.targetscan.org/vert_71/)四个数据库中均被纳入。利用miRanda数据库,根据碱基配对指数及碱基结合能量等参数预测circ-0007766-miRNA结合状态,最终确定以circ-0007766/miR-1972/HER2的ceRNA调控轴进行研究(图4A)。为了探索miR-1972在乳腺癌中的生物学效应,在SK-BR-3细胞转染了NC mimics和miR-1972 mimics(图4B),MDA-MB-231细胞转染了NC抑制剂和miR-1972抑制剂(图4D),进行细胞侵袭、迁移试验。结果显示,过表达miR-1972会抑制乳腺癌细胞的迁移和侵袭(图4C),而抑制miR-1972 则会促进细胞的迁移和侵袭(图4E)。
为了探讨circ-0007766、miR-1972和HER2之间的相互作用关系,我们首先对circ-0007766的3’UTR中与miR-1972配对结合的位点进行了突变,并分别将circ-0007766-wt和circ-0007766-mut构建到萤火虫荧光素酶报告基因载体pmiR-RB-Report中(图4F)。我们将circ-0007766-wt、circ-0007766-mut、miR-1972 mimics和miR-1972 mimics NC分别单独或共转染至293T细胞中,并进行双荧光素酶报告基因实验。结果显示,miR-1972 mimics能够显著降低circ-0007766-wt组的荧光素酶活性,而共转miR-1972 mimics对circ-0007766-mut组的荧光素酶活性无影响(图4F)。为了进一步验证circ-0007766和miR-1972是否具有直接相互作用,我们在SK-BR-3细胞和MDA-MB-231细胞中进行了RAP实验。与对照组相比,circ-0007766-wt的探针能够明显富集更多的circ-0007766,并且下拉更多的 miR-1972。而circ-0007766-mut无法下拉miR-1972,提示circ-0007766与miR-1972通过预测的结合位点直接相互作用(图4G~L)。结果表明,circ-0007766 和miR-1972之间存在直接相互作用。
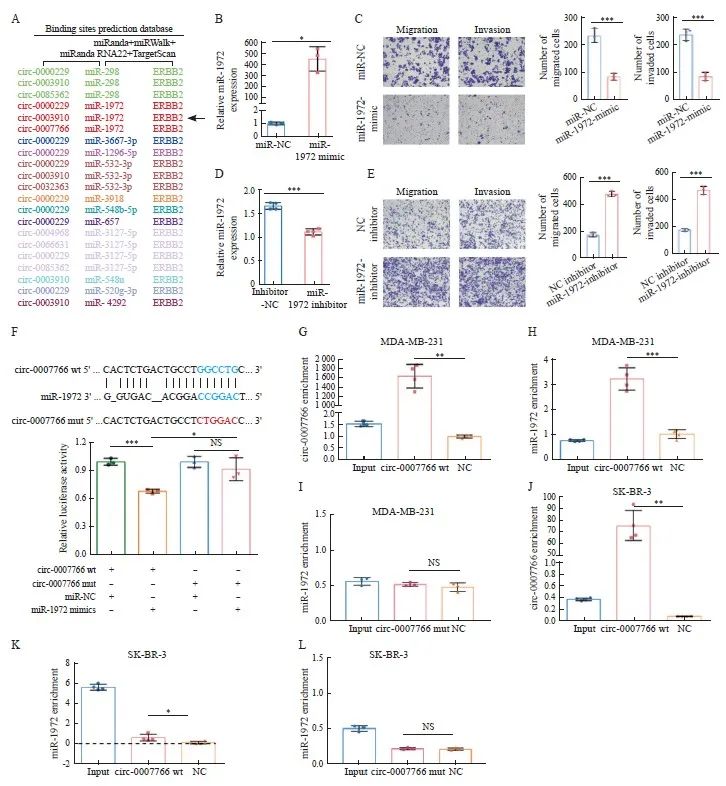
图4 Circ-0007766与肿瘤抑制基因miR-1972的相互作用
Fig. 4 Circ-0007766 interacts with miR-1972, a tumor suppressor gene
A: The schematic diagram showed the predicted circR-NA-miRNA-HER2 regulatory network. CircRNAs, miRNAs, and HER2 on the same regulatory axis were identified by the same color. B: The expression of miR-1972 in SK-BR-3 cells was evaluated after transfection with NC mimics (miR-NC) or miR-1972 mimic. C: The migration and invasion ability of SK-BR-3 cells was determined by transwell assay after transfection with miR-NC or miR-1972 mimic. D: The level of miR-1972 in MDA-MB-231 cells was determined after transfection with miR-1972 inhibitor or inhibitor NC. E: The migration and invasion ability of MDA-MB-231 cells was determined by transwell assay after transfection with miR-1972 inhibitor or inhibitor NC. F: The top of the figure described the predicted binding site between circ-0007766 and miR-1972, as well as the mutation strategy to change the binding site between circ-0007766 and miR-1972. The relative luciferase activity of miR-1972 mimics, miR-NC, circ-0007766-3'UTR-wt, or circ-0007766-3'UTR-mut co-transfected with 293T cells was shown in the figure below. G-I: The RAP assay and RTFQ-PCR assay detected the enrichment of circ-0007766 wt and circ-0007766 mut probes for circ-0007766 and miR-1972 in MDA-MB-231 cells. J-L: The RAP assay and RTFQ-PCR assay detected the enrichment of circ-0007766 wt and circ-0007766 mut probes for circ-0007766 and miR-1972 in MDA-MB-231 cells. *: P <0.05, compared with circ-0007766 mut or miR-NC; **: P<0.01, compared with circ-0007766 wt; ***: P<0.001, compared with Inhibitor-NC, miR-NC, NC inhibitor or circ-0007766 wt; NS: No significant difference. wt: Wild type; mut: Mutant.
2.5 miR-1972与HER2 mRNA结合并逆转circ-0007766对HER2表达的调控作用
本研究采用TargetScan(https://www. targetscan.org/vert_71/)数据库预测了miR-1972在HER2 mRNA 3'UTR上的潜在结合位点,从而研究了miR-1972在HER2表达中的调控作用。为了验证这一预测,我们将野生型HER2(HER2-wt)和miR-1972结合位点突变的HER2(HER2-mut)引入到萤火虫荧光素酶报告载体pmiR-Rb-report中(图5A)。随后,分别用HER2-wt、HER2-mut、miR-1972 mimic和阴性对照mimic转染293T细胞(图5A),然后进行双荧光素酶报告基因检测。与HER2-mut相比,转染miR-1972 mimics后HER2-wt的荧光素酶活性显著降低(图5A)。为了研究HER2-3'UTR与miR-1972之间的直接相互作用,使用MDA-MB-231细胞进行了RNA免疫沉淀(RIP)实验。值得注意的是,与对照组相比,miR-1972富集了更高丰度的HER2 mRNA分子的3'UTR(图5B),为miR-1972与其靶标HER2 mRNA之间的直接相互作用提供了证据。
为了确定miR-1972对HER2 mRNA和蛋白水平的影响,我们进行了RTFQ-PCR和Western blot检测。MiR-1972 mimic下调了HER2 mRNA和蛋白的表达,而miR-1972抑制剂上调了HER2 mRNA和蛋白的表达(图5C)。此外,miR-1972 mimic诱导的下调被miR-1972抑制剂部分逆转(图5C)。我们还研究了circ-0007766是否通过miR-1972影响HER2的表达。过表达circ-0007766会导致HER2 mRNA和蛋白水平上调(图5D),而敲低circ-0007766会导致HER2 mRNA和蛋白表达下调(图5E)。使用miR-1972mimic能够抑制由于过表达circ-0007766导致的HER2mRNA和蛋白水平上调作用(图5D)。反之,使用miR-1972 inhibitor能够促进由敲低circ-0007766导致的HER2 mRNA和蛋白质表达水平的抑制(图5E)。
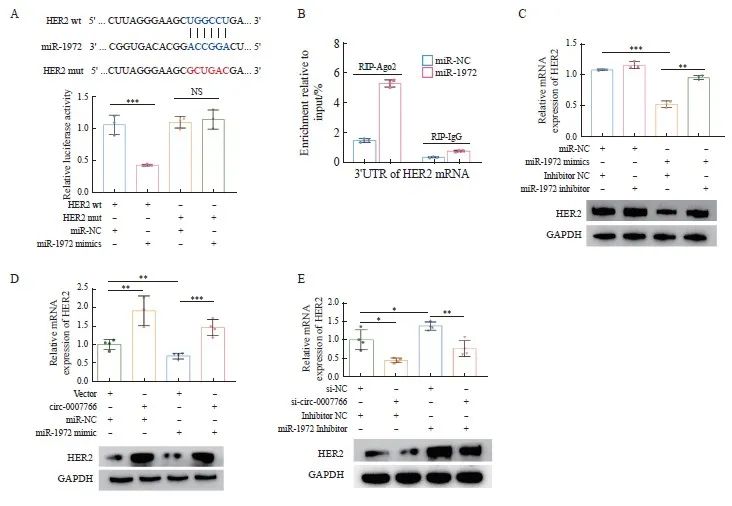
图5 MiR-1972与HER2 mRNA结合并逆转circ-0007766对HER2表达的调控作用
Fig. 5 MiR-1972 binds to HER2 mRNA and reverses the regulatory effect of circ-0007766 on HER2 expression
A: The top of the figure showed the predetermined binding sites of miR-1972 on HER2 mRNA and the mutation strategies for the binding sites of HER2 mRNA with miR-1972. The bottom of the figure showed the relative luciferase activity in 293T cells after co-transfection with miR-1972 mimics, miR-NC, HER2-3'UTR-mut (HER2-mut) or HER2-3'UTR-wt (HER2-wt). B: After co-transfection with miR-NC or miR-1972 mimics, RIP assay was performed in MDA-MB-231 cells, and HER2 mRNA 3'UTR was measured by RTFQ-PCR. C: RTFQ-PCR and Western blot confirmed the expression levels of HER2 mRNA and protein in MDA-MB-231 cells after co-transfection with miR-NC+NC, miR-NC+miR-1972, miR-1972+NC or their combinations, and specific inhibitors. D: RTFQ-PCR and Western blot showed the expression levels of HER2 mRNA and protein in MDA-MB-231 cells after co-transfection with vector+miR-NC, circ-0007766+miR-NC, vector+miR-1972 mimics or circ-0007766+miR-1972 mimics. E: RTFQ-PCR and Western blot showed the expression levels of HER mRNA and protein in SK-BR-3 cells after co-transfection with si-NC+inhibitor NC, si-circ-0007766+inhibitor NC, si-NC+miR-1972 inhibitor or si-circ-0007766+miR-1972 inhibitor. *: P<0.05, compared with si-NC or inhibitor NC; **: P<0.01, compared with inhibitor NC, vector, miR-NC or si-NC; ***: P<0.001, compared with miR-NC or vector; NS: No significant difference.
2.6 Circ-0007766通过miR-1972促进乳腺癌细胞的迁移和侵袭
为了研究circ-0007766能否通过miR-1972调控乳腺癌细胞迁移和侵袭,我们分别在MDA-MB-231和SK-BR-3中进行transwell迁移和侵袭实验。细胞迁移试验的结果表明,上调circ-0007766能显著增强乳腺癌细胞的迁移能力,而过表达miR-1972则会抑制细胞的迁移。同时过表达circ-0007766和miR-1972后,这种由miR-1972过表达造成的迁移和侵袭的抑制得到挽回(图6A)。细胞侵袭试验中观察到,circ-0007766的过表达促进了细胞的侵袭,而miR-1972的上调则削弱了这种能力。然而,当同时过表达circ-0007766和miR-1972时,miR-1972上调对细胞侵袭的抑制作用得以恢复(图6A)。此外,本研究在SK-BR-3细胞中对circ-0007766和(或)miR-1972进行敲低,以评估其迁移和侵袭能力的变化。研究结果表明,敲低circ-0007766会阻碍细胞迁移和侵袭;相反,敲低miR-1972会促进这些过程。值得注意的是,与单独敲低相比,同时敲低circ-0007766和miR-1972可部分恢复细胞的迁移/侵袭能力(图6B)。
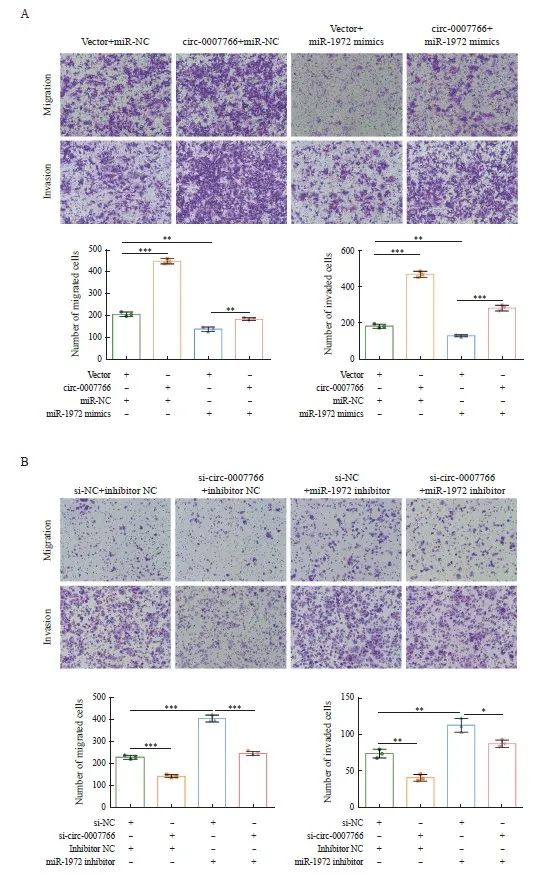
图6 Circ-0007766通过miR-1972促进乳腺癌细胞迁移和侵袭
Fig. 6 Circ-0007766 promotes breast cancer cell migration and invasion through miR-1972
A: The migration and invasion potential of MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with the transfection vector+miR-NC, circ-0007766+miR-NC, vector+miR-1972 mimic or circ-0007766+miR-1972 mimic was evaluated using a transwell migration and invasion assay. B: The migration and invasion ability of SK-BR-3 cells after transfection with si-NC+inhibitors NC, si-circ-0007766+inhibitors NC, si-NC+miR-1972 inhibitor or si-circ-0007766+miR-1972 inhibitor was evaluated using a transwell assay. *: P<0.05, compared with si-NC; **: P<0.01, compared with vector, miR-NC, si-NC or inhibitor NC; ***: P<0.001, compared with vector, inhibitor NC or si-NC.
2.7 乳腺癌细胞中circ-0007766与miR-1972的表达水平呈负相关
上述研究提示,circ-0007766和miR-1972通过ceRNA机制调节HER2的表达水平,我们推测三者在乳腺癌细胞中的表达水平具有一定的相关性。首先,如TCGA(https://www.cancer. gov/about-nci/organization/ccg/research/structural-genomics/tcga)和人类蛋白质图谱数据库(https://www.proteinatlas.org/)分析结果所示, HER2 mRNA和蛋白质在乳腺癌组织中的表达显著增加(图7A~C)。RTFQ-PCR分析显示,在代表不同分子亚型的5种乳腺癌细胞系中,circ-0007766(图1C)和miR-1972(图7D)都有可检测到的表达水平。与SK-BR-3细胞相比,miR-1972在MDA-MB-231细胞中的表达水平明显更高,与circ-0007766的表达呈负相关(图7D)。此外,在检测的5种乳腺癌细胞系中,circ-0007766和miR-1972的表达水平都呈显著负相关(图7E)。上述发现表明,circ-0007766能特异性靶向miR-1972,从而阻碍miR-1972对HER2表达的调控作用。这一机制可能在很大程度上导致了乳腺癌中HER2表达水平的上调。
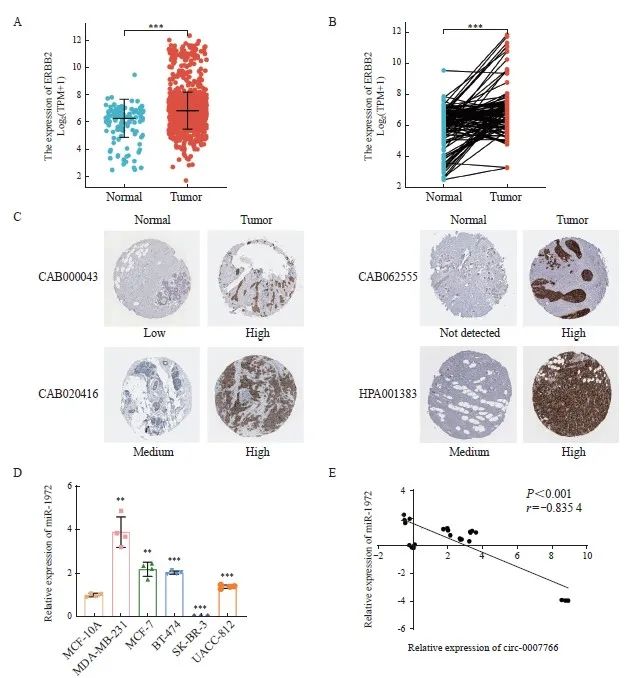
图7 乳腺癌组织中HER2的表达与乳腺癌细胞中circ-0007766和miR-1972表达的相关性
Fig. 7 Expression of HER2 in breast cancer tissues and correlation of circ-0007766 and miR-1972 expression in breast cancer cells
A: Expression of HER2 mRNA in unpaired TCGA breast cancer/normal tissue. B: Expression of HER2 mRNA in paired TCGA-derived breast cancer tissue and normal tissue. C: Expression of HER2 protein in breast cancer and normal tissue, shown by representative immunohistochemical staining images from the Human Protein Atlas. D: Expression of miR-1972 in different breast cancer cells and normal breast cancer cell MCF10A. E: Analysis of the correlation between circ-0007766 and miR-1972 expression using data from Fig. 1C and Fig. 6D. Circ-0007766 and miR-1972 mRNA relative expression levels were converted to log2 scale. **: P<0.01, compared with MCF10A; ***: P<0.001, compared with normal or MCF10A.
3 讨 论
HER2型乳腺癌发展进程快、易转移和复发。HER2的异常表达是该亚型乳腺癌的主要特征。HER2能够与自身或与HER家族的其他成员形成同源或异源二聚体,从而促进乳腺癌细胞分裂、增殖、迁移等生物学行为。HER2的异常扩增也是乳腺癌患者生存率的负相关因子,并且其表达阳性代表着乳腺癌的复发转移风险升为中危或高危[23-26]。因此,对于HER2表达调控机制的深入理解对于HER2阳性乳腺癌的靶向治疗和耐药机制研究均具有重要意义。
CircRNA是一类结构稳定、表达量丰富、具有组织特异性和高保守性的非编码RNA[27-28]。以circRNA为基础的circRNA-蛋白质互作网络和信号调控网络在肿瘤转移进程中发挥重要作用[29-30]。CircACTN4能够与FIR竞争性结合上游元件结合蛋白1(far-upstream element binding protein 1,FUBP1),促进MYC基因的转录激活,从而促进乳腺癌的进展[31]。CircRNF20结合miR-487a并作为其分子海绵,抑制miR-487a介导的对缺氧诱导因子-1(hypoxia inducible factor-1,HIF-1α)的负调控作用,促进HIF-1α对己糖激酶Ⅱ(hexokinase Ⅱ,HK2)的转录激活作用,从而促进乳腺癌的增殖和沃伯格效应[32]。本研究发现,过表达circ-0007766能够促进TNBC细胞MDA-MB-231的迁移和侵袭,而miR-1972会抑制MDA-MB-231的迁移和侵袭。由于circ-0007766在MDA-MB-231中的内源性表达水平极低(图1G),因此circ-0007766可能不是驱动TNBC细胞迁移和侵袭的主要致癌基因,其在HER2阳性乳腺癌细胞中主要通过调控HER2的表达发挥促转移作用,但circRNA自身具有多样化的分子调控机制,circ-0007766也可能通过调节信号转导通路、编码蛋白质或多肽、调节基因转录或选择性剪切促进转移。在HER2阳性乳腺癌细胞中,miR-1972主要通过靶向抑制HER2 mRNA的表达发挥抑癌基因作用,然而,TNBC细胞中HER2 mRNA的表达水平极低,miR-1972缺少直接作用靶点,因此miR-1972在TNBC细胞中的抑癌作用也可能通过影响细胞外基质和黏附分子、参与信号转导通路以及外泌体传输途径实现。
本研究发现miR-1972/HER2信号轴是circ-0007766实现促癌效应的重要途径。这一结论不仅拓宽了对circ-0007766促进乳腺癌转移机制的理解,也表明circRNA对母本基因的编码蛋白的调控方式具有多样性。然而,这两项研究均关注了circ-0007766在细胞质中的生物学功能,通过FISH实验我们还发现部分circ-0007766分布于细胞核。由于在细胞核中的circRNA主要参与转录复合体的组装和基因调控元件的激活,我们推测circ-0007766可能参与ERBB2基因的转录激活。
CircRNA-miRNA-mRNA调控网络是一种内源性竞争RNA作用模式。前期研究表明,miR-1972可作为多种lncRNA,包括LINC01207和lncRNA DANCR的分子海绵,分别调控LASP1和ROCK1的表达,在前列腺癌和肉瘤的发生、发展中发挥重要作用[18-19]。尽管Guo等[33]利用circRNA芯片结合生物信息学建模预测了circRNA_021412/miR-1972/LPIN1调控轴可能在Hepatic Steatosis中发挥重要作用,但circ-0007766是目前唯一报道的、经过实验验证的miR-1972的上游circRNA调控因子。由于miR-1972在包括乳腺癌在内的多种恶性肿瘤中低表达,如何通过转录激活的方式上调miR-1972的表达水平,进而抑制其下游HER2、LASP1和ROCK1等重要致癌基因的表达,在未来具有一定的研究价值。
BaseScope基于信号放大和背景信号抑制技术[34],将组织样本中的单个RNA可视化呈现。该实验技术具备高度敏感性、高特异性和高信噪比的优点,并且与PCR、免疫组织化学的检测结果都有很好的一致性。在本研究中,阳性信号探针和阴性对照组的染色结果均符合预期,表明实验过程无问题。结果显示,circ-0007766仅在部分乳腺癌组织中高表达,而在正常乳腺组织中几乎不表达,我们推测circ-0003910的表达水平可能在特定乳腺癌样本类型中受到特定基因元件的调控,但其具体机制仍不清楚。此外,circ-0007766在HER2阳性和HER2阴性乳腺癌组织中的表达水平的差异不如在细胞水平显著,其可能原因是细胞水平的实验结果无法全面真实地反映乳腺癌患者的个体差异状态。
综上所述,circ-0007766在HER2型乳腺癌细胞和组织中呈高表达,通过miR-1972分子海绵促进HER2型乳腺癌细胞的迁移和侵袭,从而增强HER2的表达水平,起到癌基因效应。本研究为进一步揭示以HER2为基础的复杂乳腺癌转移调控网络提供了新的思路。
利益冲突声明:所有作者均不存在利益 冲突。
作者贡献声明:赵峻秀负责文章撰写、实验设计及验证、实验数据整理分析,朱艺负责文章撰写、数据收集整理、实验验证,宋筱羽负责数据统计分析、文献检索,柘钞负责文献检索,肖雨晗进行文章的英文翻译工作,刘云多负责整理参考文献,李林海负责选题、文章审校,肖斌负责实验设计、文章审阅与修订。
[参考文献]
[1] YEO S K, GUAN J L. Breast cancer: multiple subtypes within a tumor? [J]. Trends Cancer, 2017, 3(11): 753-760.
[2] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249.
[3] LIU Y, ZHU X Z, XIAO Y, et al. Subtyping-based platform guides precision medicine for heavily pretreated metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: the FUTURE phase Ⅱ umbrella clinical trial[J]. Cell Res, 2023, 33(5): 389-402.
[4] HARBECK N, GNANT M. Breast cancer l[J]. Lancet, 2017, 389(10074): 1134-1150.
[5] OH D Y, BANG Y J. HER2-targeted therapies-a role beyond breast cancer[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2020, 17: 33-48.
[6] TAPIA M, HERNANDO C, MARTÍNEZ M T, et al. Clinical impact of new treatment strategies for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer patients with resistance to classical anti-HER therapies[J]. Cancers, 2023, 15(18): 4522.
[7] YE P, WANG Y R, LI R Q, et al. The HER family as therapeutic targets in colorectal cancer[J]. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2022, 174: 103681.
[8] SCERRI J, SCERRI C, SCHÄFER-RUOFF F, et al. PKCmediated phosphorylation and activation of the MEK/ERK pathway as a mechanism of acquired trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2022, 13: 1010092.
[9] HARPER K L, SOSA M S, ENTENBERG D, et al. Mechanism of early dissemination and metastasis in HER2+ mammary cancer[J]. Nature, 2016, 540(7634): 588-592.
[10] LO P K, KANOJIA D, LIU X, et al. CD49f and CD61 identify HER2/neu-induced mammary tumor-initiating cells that are potentially derived from luminal progenitors and maintained by the integrin-TGFβ signaling[J]. Oncogene, 2012, 31(21): 2614-2626.
[11] NAMI B, WANG Z X. HER2 in breast cancer stemness: a negative feedback loop towards trastuzumab resistance[J]. Cancers, 2017, 9(5): 40.
[12] LUO Z, RONG Z Y, ZHANG J M, et al. Circular RNA circCCDC9 acts as a miR-6792-3p sponge to suppress the progression of gastric cancer through regulating CAV1 expression[J]. Mol Cancer, 2020, 19(1): 86.
[13] WU Y Z, XIE Z A, CHEN J X, et al. Circular RNA circTADA2A promotes osteosarcoma progression and metastasis by sponging miR-203a-3p and regulating CREB3 expression[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 73.
[14] LI J, MA M G, YANG X S, et al. Circular HER2 RNA positive triple negative breast cancer is sensitive to pertuzumab[J]. Mol Cancer, 2020, 19(1): 142.
[15] 张 帅, 夏文佳, 董高超, 等. 环状RNA分子circ_0007766通过上调细胞周期相关蛋白cyclin D1/cyclin E1/CDK4的表达促进肺腺癌细胞增殖[J]. 中国肺癌杂志, 2019, 22(5): 271-279.
ZHANG S, XIA W J, DONG G C, et al. Cyclic RNA molecule circ_0007766 promotes the proliferation of lung adenocarcinoma cells by up-regulating the expression of cyclin D1/cyclin E1/ CDK4[J]. Chin J Lung Cancer, 2019, 22(5): 271-279.
[16] XU W G, ZHOU B, WU J, et al. Circular RNA hsacirc- 0007766 modulates the progression of Gastric Carcinoma via miR-1233-3p/GDF15 axis[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2020, 17(11): 1569-1583.
[17] GUO J, PAN H. Long non-coding RNA LINC01125 enhances cisplatin sensitivity of ovarian cancer via miR-1972[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2019, 25: 9844-9854.
[18] WANG S G, QIU J G, WANG L P, et al. Long non-coding RNA LINC01207 promotes prostate cancer progression by downregulating microRNA-1972 and upregulating LIM and SH3 protein 1[J]. IUBMB Life, 2020, 72(9): 1960-1975.
[19] WANG Y, ZENG X D, WANG N N, et al. Long noncoding RNA DANCR, working as a competitive endogenous RNA, promotes ROCK1-mediated proliferation and metastasis via decoying of miR-335-5p and miR-1972 in osteosarcoma[J]. Mol Cancer, 2018, 17(1): 89.
[20]朱 艺, 肖 斌, 刘嘉慧, 等. Circ-0003910在HER2阳性乳腺癌中的表达、定位、生物学作用及蛋白质组学研究[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2022, 32 (10): 979-989.
ZHU Y, XIAO B, LIU J H, et al. Expression, localization, biological role and proteomics study of circ-0003910 in HER2-positive breast cancer[J]. China Oncol, 2022, 32(10): 979-989.
[21]HUANG L, MA J, CUI M. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0001598 promotes programmed death-ligand-1-mediated immune escape and trastuzumab resistance via sponging miR-1184 in breast cancer cells[J]. Immunol Res, 2021, 69(6): 558-567.
[22]HOSONAGA M, ARIMA Y, SUGIHARA E, et al. Effect of heterogeneity of HER2 expression on brain metastases of breast cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2012, 30(15_suppl): 635.
[23]JORDAN N V, BARDIA A, WITTNER B S, et al. HER2 expression identifies dynamic functional states within circulating breast cancer cells[J]. Nature, 2016, 537: 102-106.
[24]JIN J, CAO J, LI B, et al. Landscape of DNA damage response gene alterations in breast cancer: a comprehensive investigation[J]. Cancer, 2023, 129(6): 845-859.
[25]ZHANG P, ZHANG Q Y, TONG Z S, et al. Dalpiciclib plus letrozole or anastrozole versus placebo plus letrozole or anastrozole as first-line treatment in patients with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer (DAWNA-2): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2023, 24(6): 646-657.
[26]中国抗癌协会乳腺癌专业委员会, 中华医学会肿瘤学分会乳腺肿瘤学组. 中国抗癌协会乳腺癌诊治指南与规范(2024年版)[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2023, 33(12): 1092-1187.
The Society of Breast Cancer China Anti-Cancer Association, Breast Oncology Group of the Oncology Branch of the Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for breast cancer diagnosis and treatment by China Anti-Cancer Association (2024 edition)[J]. China Oncol, 2023, 33(12): 1092-1187.
[27]ZHENG Q P, BAO C Y, GUO W J, et al. Circular RNA profiling reveals an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging multiple miRNAs[J]. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 11215.
[28]KRISTENSEN L S, ANDERSEN M S, STAGSTED L V W, et al. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs[J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2019, 20(11): 675-691.
[29]WANG Q, WANG H Z, ZHAO X M, et al. Transcriptome sequencing of circular RNA reveals the involvement of hsa-SCMH1_0001 in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2024, 30(3): e14435.
[30]LIU B Y, GONG Y J, JIANG Q Y, et al. Hsa_circ_0014784-induced YAP1 promoted the progression of pancreatic cancer by sponging miR-214-3p[J]. Cell Cycle, 2023, 22(13): 1583-1596.
[31]WANG X S, XING L, YANG R, et al. The circACTN4 interacts with FUBP1 to promote tumorigenesis and progression of breast cancer by regulating the expression of proto-oncogene MYC[J]. Mol Cancer, 2021, 20(1): 91.
[32]CAO L L, WANG M, DONG Y J, et al. Circular RNA circRNF20 promotes breast cancer tumorigenesis and Warburg effect through miR-487a/HIF-1α/HK2[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(2): 145.
[33]GUO X Y, HE C X, WANG Y Q, et al. Circular RNA profiling and bioinformatic modeling identify its regulatory role in hepatic steatosis[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2017, 2017: 5936171.
[34]KIRBY E, TSE W H, PATEL D, et al. First steps in the development of a liquid biopsy in situ hybridization protocol to determine circular RNA biomarkers in rat biofluids[J]. Pediatr Surg Int, 2019, 35(12): 1329-1338.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言
















#乳腺癌# #Circ-0007766# #miR-1972#
40