这才是极具价值的临床科研选题:预后标记、观察指标!美国68项在研胰腺炎基金的启发(2024)
2024-10-30 Hanson临床科研 Hanson临床科研 发表于上海
我们仅对美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)资助的在研胰腺炎相关项目进行梳理,希望给同仁们的选题思路提供一点启发。
胰腺炎(Pancreatitis)是一种胰腺发炎的疾病,胰腺是一个位于胃后部的腺体,主要功能是分泌消化酶和激素,如胰岛素。胰腺炎通常可以表现为急性或慢性两种形式:
-
急性胰腺炎:通常表现为突发的严重腹部疼痛,疼痛可能放射到背部。伴有恶心、呕吐、发热和心跳加速。急性发作可以由多种原因引起,如长期酗酒、胆石阻塞等。
-
慢性胰腺炎:特征为胰腺长期炎症,导致胰腺功能逐渐丧失,常表现为反复的腹痛、消化不良和体重下降。慢性胰腺炎可能导致胰腺组织硬化和瘢痕形成。
尽管近年来在胰腺炎的诊断和治疗方面取得了显著进展,但仍存在一些重要而未解决的临床问题:
-
早期诊断:尽管有进步,早期诊断胰腺炎仍具挑战性,特别是在症状不典型的情况下。提高早期诊断能力可以减少并发症和改善预后。
-
疼痛管理:胰腺炎的疼痛管理仍是一个重要问题,尤其是在慢性胰腺炎患者中,有效的疼痛控制方案有限。
-
治疗策略:当前治疗主要依赖对症治疗,缺乏针对性的治疗方法来逆转或停止疾病进程。研发新的药物和治疗方法以更有效地治疗胰腺炎是迫切需要的。
-
长期并发症:如何管理和预防胰腺炎患者的长期并发症,包括糖尿病和消化系统问题,仍是临床上的一个难题。
胰腺炎的研究和治疗领域仍需更多的创新和突破,以改善患者的临床管理和生活质量。
我们仅对美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)资助的在研胰腺炎相关项目进行梳理,希望给同仁们的选题思路提供一点启发。
2024年,以“Pancreatitis”为检索词、在题目中进行检索,美国NIH针对胰腺炎的在研有68项。
一,谁获得了这些研究?
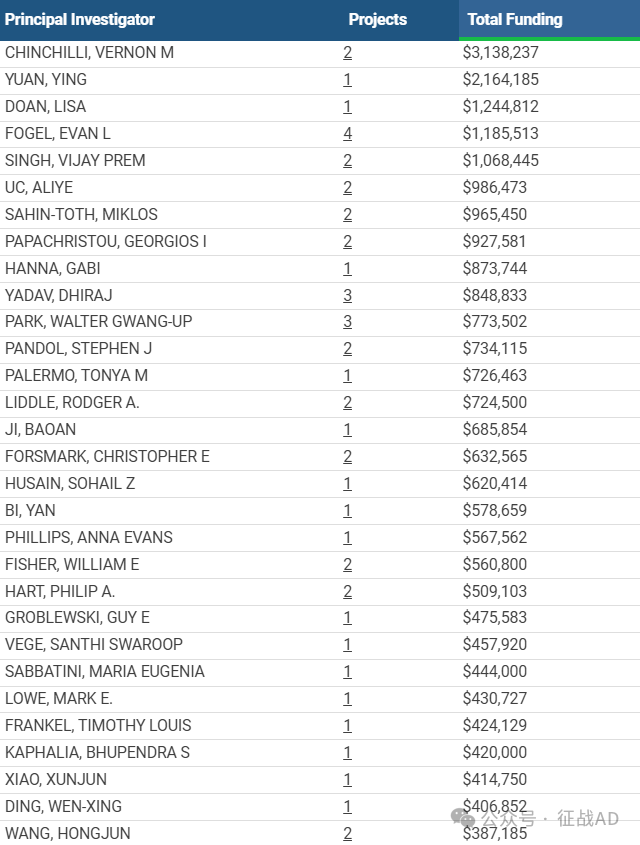
1,在研胰腺炎基金最多的PI
-
PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIV HERSHEY MED CTR 的 CHINCHILLI, VERNON M
-
UNIVERSITY OF TX MD ANDERSON CAN CTR 的 YUAN, YING
-
NEW YORK UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE 的 DOAN, LISA
-
INDIANA UNIVERSITY INDIANAPOLIS 的 FOGEL, EVAN L
-
MAYO CLINIC ARIZONA 的 SINGH, VIJAY PREM
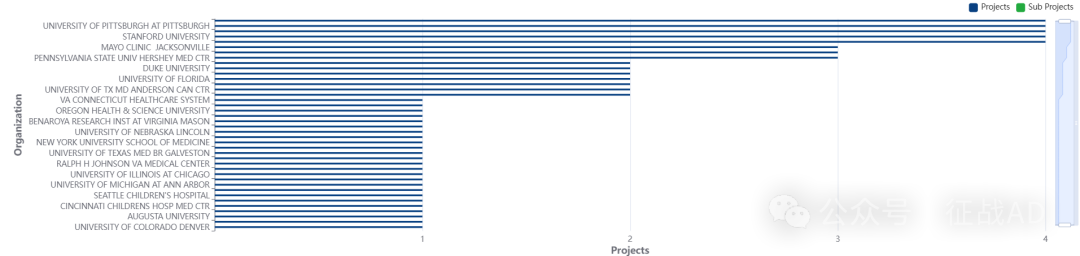
2,胰腺炎基金最多的研究机构
-
宾夕法尼亚州立大学赫尔希医学中心
-
德克萨斯大学 MD 安德森癌症中心
-
加州大学洛杉矶分校
-
梅奥诊所杰克逊维尔
-
俄亥俄州立大学等
二,胰腺炎研究热点是什么?
胰腺炎研究领域总览(根据关键词)
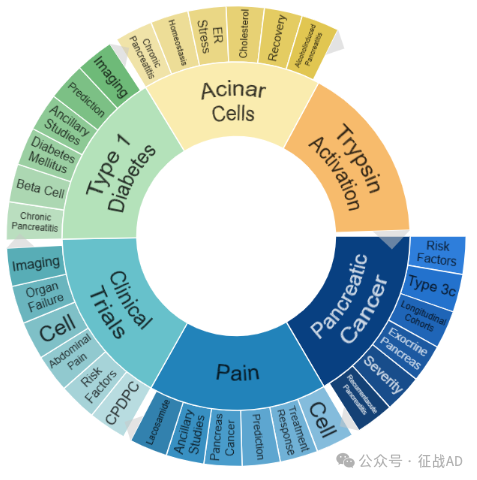
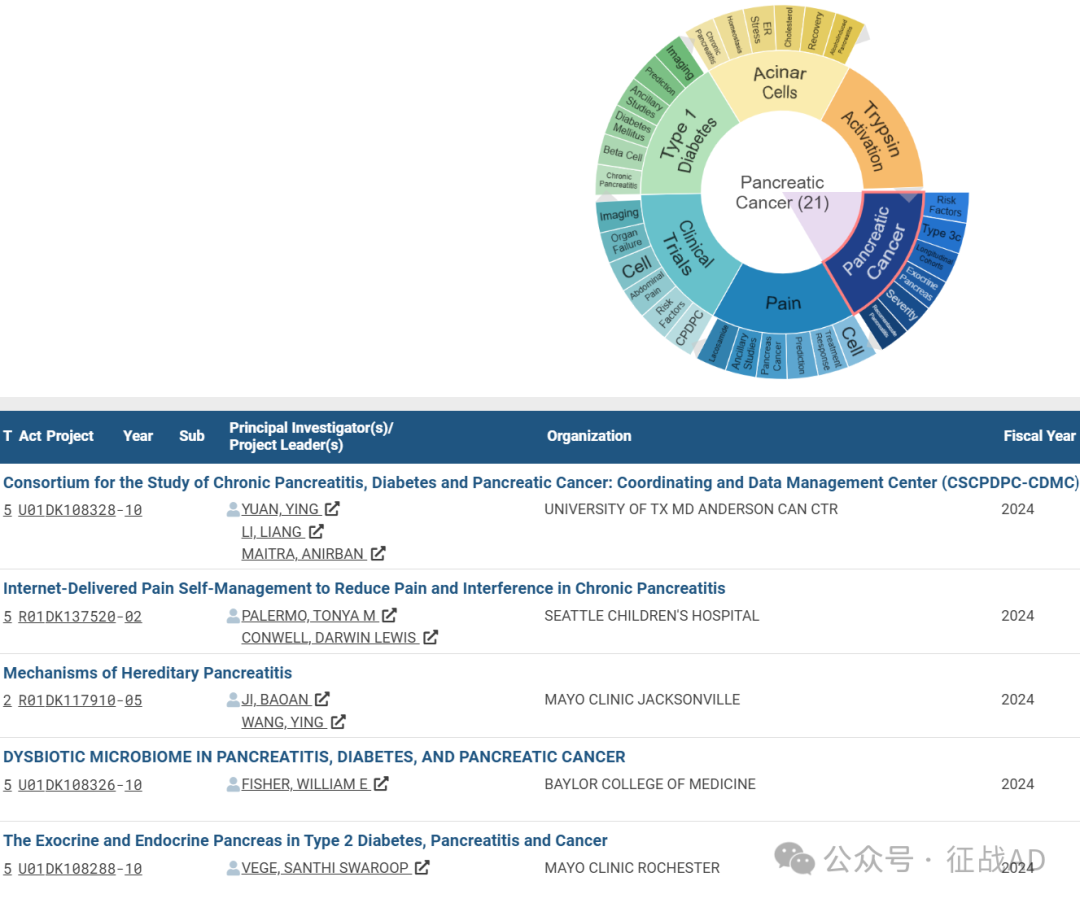
A,关于胰腺癌(Pancreatic Cancer)的研究项目最多
有 21 项在研基金涉及到了胰腺癌,关注最多的方面包括风险因素(Risk Factor)、Type 3c分型、纵向队列(Longitudinal Cohorts)、外分泌胰腺(Exocrine Pancreas)、严重程度(Severity)、复发性急性胰腺炎(Recrrentacute Pancreatits)等研究。
B,关于疼痛(Pain)的研究项目
有 20 项在研基金涉及到了疼痛,关注最多的方面包括细胞、治疗反应(Treatment Response)、预测(Prediction)、胰腺癌(Pancreas Cancer)、辅助研究(Ancillary Studies)、Lacosamide等研究。
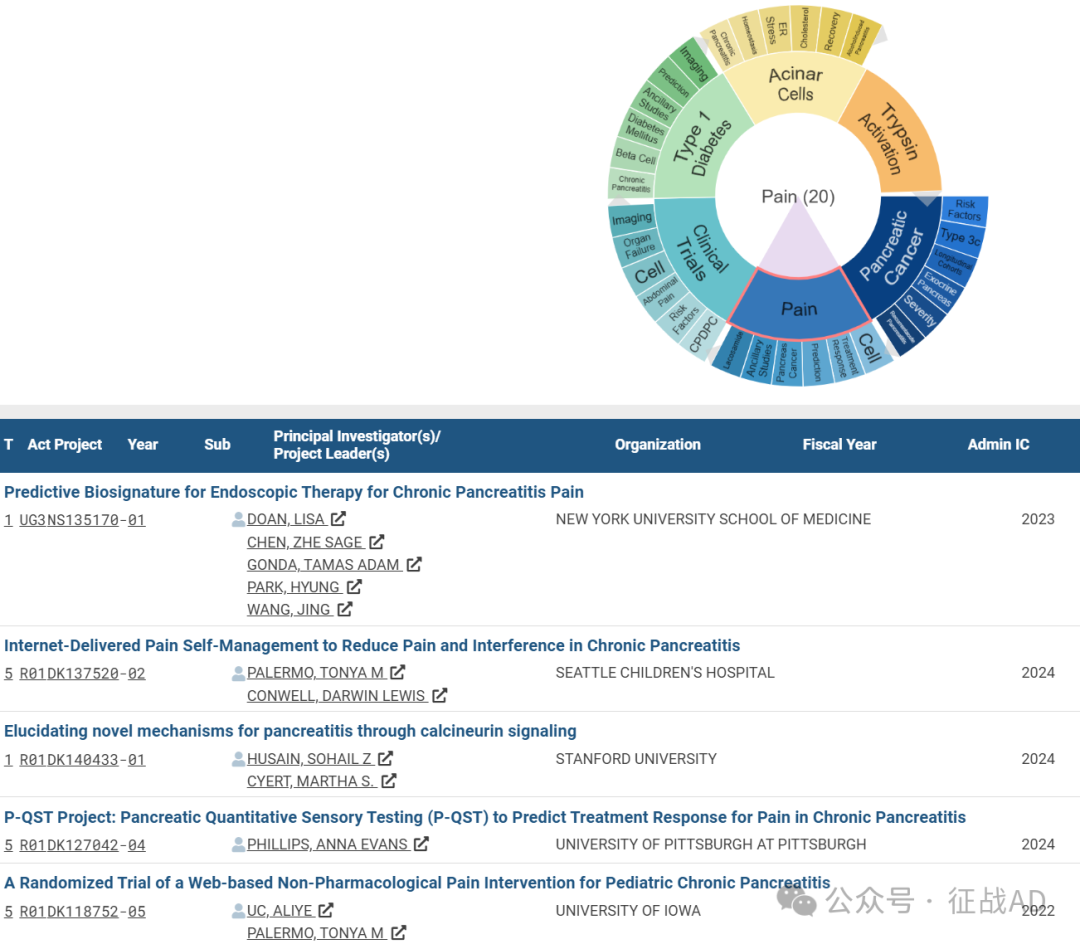
C,关于临床试验(Clinical Trails)的研究项目
有 19 项在研基金涉及到了临床试验,关注最多的方面包括影像学(Imaging)、器官特征(Organ Feature)、细胞、腹痛(Abdominal Pain)、风险因素、CPDPC等研究。
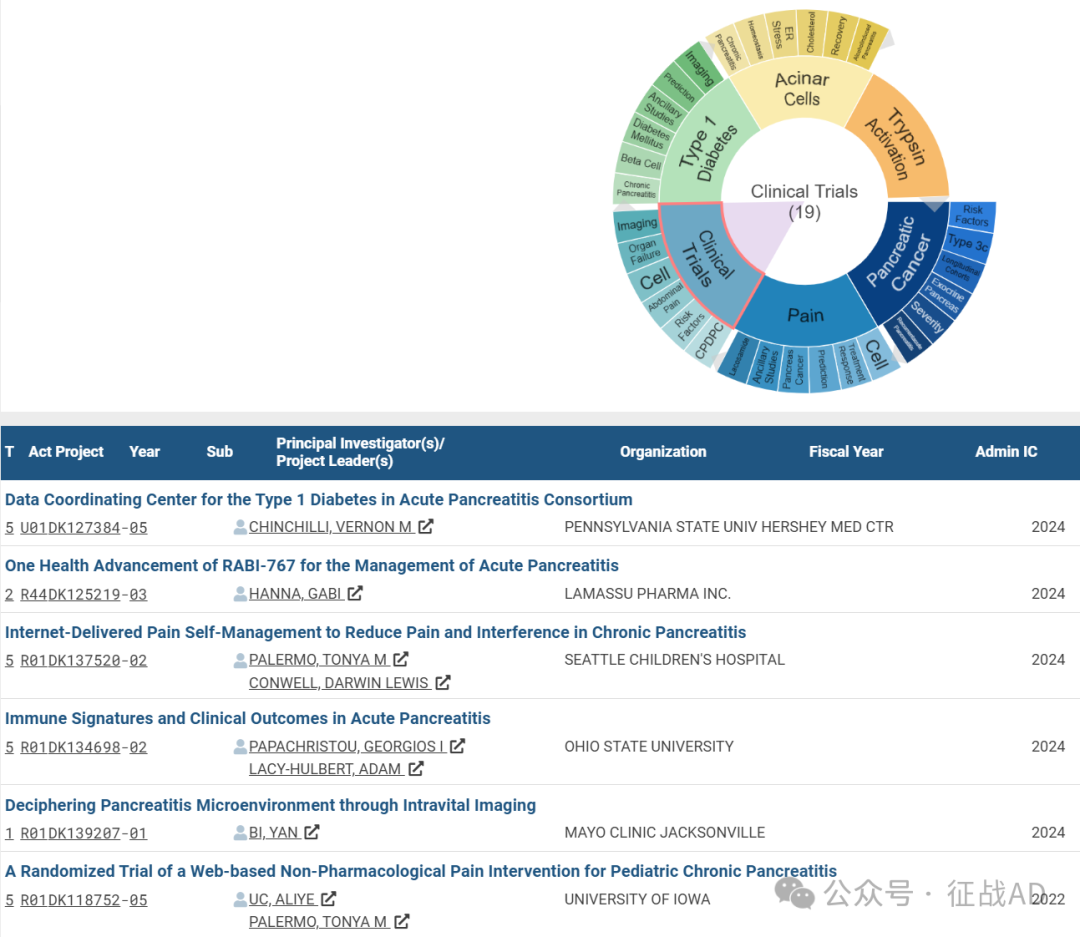
其他胰腺炎研究大的方向还包括1型糖尿病(Type 1 Diabetes)、腺泡细胞(Acinar Cells)、胰蛋白酶激活(Trypsin Activation)等。
三,借鉴与突破
我们也分享在胰腺炎领域的几项课题摘要,希望对同仁们有所启发。
A,Predictive Biosignature for Endoscopic Therapy for Chronic Pancreatitis Pain
In this proposal we aim to use machine learning to develop multimodal predictive biosignatures for pain response to endoscopic therapies utilizing electroencephalography (EEG), quantitative sensory testing (QST), and biopsychosocial variables.
Our study is founded on the premise that while pancreatic pathology initially drives pain, over time alterations in central pain processing may become a dominant driver of pain in some patients with CP, making them resistant to therapies aimed at the periphery. Neuroimaging with EEG, sensory testing with QST, and psychosocial questionnaires assess central vs peripheral changes in pain processing. Combining these tools in a multimodal biosignature can improve sensitivity and specificity of prediction and advance s election of appropriate treatment of CP pain. In the UG3 phase of our proposal, we will measure EEG and QST and assess psychosocial factors in ~100 patients with alcohol-induced CP pain undergoing endoscopic therapy as part of standard clinical care. Using machine learning algorithms, we will extract features and develop candidate predictive biosignatures for pain treatment response to endoscopic therapy. In the UH3 phase we will validate and select the biosignature with the highest area under the curve met ric in a new cohort of patients.
Our success will have direct clinical impact, improving care of this refractory chronic pain syndrome and enabling similar studies in other chronic abdominal pain syndromes.
B, Diabetes RElated to Acute Pancreatitis and its Mechanisms: Metabolic Outcomes Using Novel CGM Metrics (DREAM-ON)
The Type 1 Diabetes and Acute Pancreatitis Consortium (T1DAPC): The overall goals of the T1DAPC are to describe the risk for and mechanisms of diabetes mellitus occurring after one or more episodes of acute pancreatitis. Secondary objectives include defining the natural history of acute pancreatitis, the clinical risk factors that predict development of diabetes and pre-diabetes, the natural history of beta cell function after acute pancreatitis, and the potential contribution of an altered immune state to the increased risk for diabetes after acute pancreatitis. These objectives are being addressed the ongoing, prospective, observational T1DAPC study entitled “Diabetes RElated to Acute Pancreatitis and its Mechanisms (DREAM)”.
DREAM-ON: This ancillary study pilot proposal, entitled “Diabetes RElated to Acute Pancreatitis and its Mechanisms: Metabolic Outcomes Using Novel CGM Metrics (DREAM-ON)” which will be conducted in participants enrolled in the DREAM study, will test whether continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) is clinically useful to predict risk for developing diabetes, the need for insulin therapy among those who develop diabetes and whether CGM can provide insight into the diabetes subtype among patients who have experienced an episode of acute pancreatitis. Thus, the results of this ancillary study will complement and extend the primary research questions in the DREAM study.
Specific Aims: Aim 1: To perform CGM in all participants in the DREAM study in conjunction with their scheduled visits at months 3, 12, 24 and subsequent annual visits and to determine if CGM metrics predict incident pre-diabetes and DM. Aim 2: To determine if CGM metrics predict need for insulin therapy in patients who develop DM after AP. Aim 3: To determine whether CGM metrics correlate with measures of insulin secretion and insulin resistance derived from the OGTT, MMT and FSIVGTT, and can be used as a surrogate to predict diabetes subtype.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言















#胰腺炎# #美国国立卫生研究院#
54